There are three main steps of urine formation: glomerular filtration, reabsorption, and secretion. These processes ensure that only waste and excess water are removed from the body. 1. The Glomerulus Filters Water and Other Substances from the Bloodstream Each kidney contains over 1 million tiny structures called nephrons.
Urine Creation
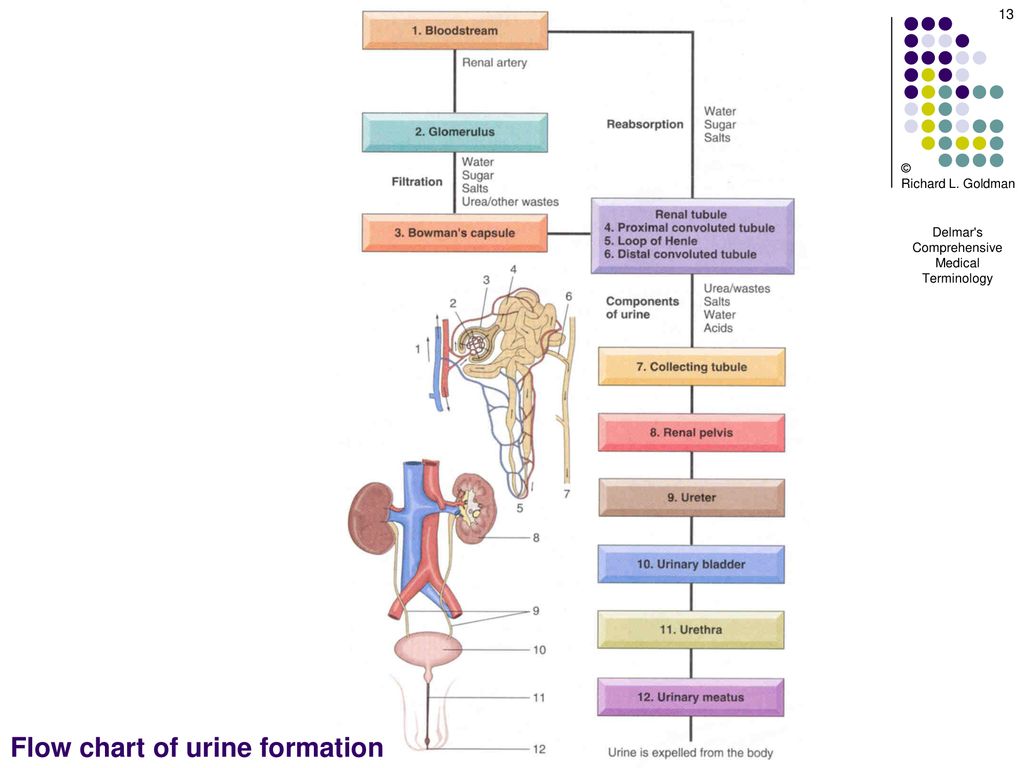
Physiology of Urine formation. There are three stages involved in the process of urine formation. They are-. 1. Glomerular filtration or ultra-filtration. 2. Selective reabsorption. 3. Tubular secretion.

Source Image: slideplayer.com
Download Image
The filtrate not recovered by the kidney is the urine that will be eliminated. It is the GFR times the fraction of the filtrate that is not reabsorbed (0.8 percent). 110*.008 = 0.9 mL urine /min. Multiply urine/min times 60 minutes times 24 hours to get daily urine production. 0.9*60*24 = 1296 mL/day urine. Table 25.4.
Source Image: slideplayer.com
Download Image
Understanding Urine Formation: A Comprehensive Flow Chart The formation process occurs in 3 steps or phases: Glomerular Filtration Tubular Reabsorption Tubular Secretion Anatomy of the Nephron (Source: sites.google.com) The anatomy of the nephron is important to understand the urine formation process. Each nephron is made up of two parts: Renal Corpuscle Renal Tubule

Source Image: m.youtube.com
Download Image
10 Steps To Describe The Formation Of Urine
The formation process occurs in 3 steps or phases: Glomerular Filtration Tubular Reabsorption Tubular Secretion Anatomy of the Nephron (Source: sites.google.com) The anatomy of the nephron is important to understand the urine formation process. Each nephron is made up of two parts: Renal Corpuscle Renal Tubule Nephrons: The Functional Unit. Nephrons take a simple filtrate of the blood and modify it into urine. Many changes take place in the different parts of the nephron before urine is created for disposal. The term forming urine will be used hereafter to describe the filtrate as it is modified into true urine.
Form 4 Biology – excretion (formation of urine) – YouTube
Jan 17, 2023Urine is formed in three steps: filtration, reabsorption, and secretion. Learning Objectives Summarize the steps in urine formation Key Points Filtration involves the transfer of soluble components, such as water and waste, from the blood into the glomerulus. Renal Tubular Acidosis – NIDDK

Source Image: niddk.nih.gov
Download Image
Formation of Urine – Nephron Function, Animation. – YouTube Jan 17, 2023Urine is formed in three steps: filtration, reabsorption, and secretion. Learning Objectives Summarize the steps in urine formation Key Points Filtration involves the transfer of soluble components, such as water and waste, from the blood into the glomerulus.

Source Image: m.youtube.com
Download Image
Urine Creation There are three main steps of urine formation: glomerular filtration, reabsorption, and secretion. These processes ensure that only waste and excess water are removed from the body. 1. The Glomerulus Filters Water and Other Substances from the Bloodstream Each kidney contains over 1 million tiny structures called nephrons.
Source Image: visiblebody.com
Download Image
Understanding Urine Formation: A Comprehensive Flow Chart The filtrate not recovered by the kidney is the urine that will be eliminated. It is the GFR times the fraction of the filtrate that is not reabsorbed (0.8 percent). 110*.008 = 0.9 mL urine /min. Multiply urine/min times 60 minutes times 24 hours to get daily urine production. 0.9*60*24 = 1296 mL/day urine. Table 25.4.

Source Image: pinterest.com
Download Image
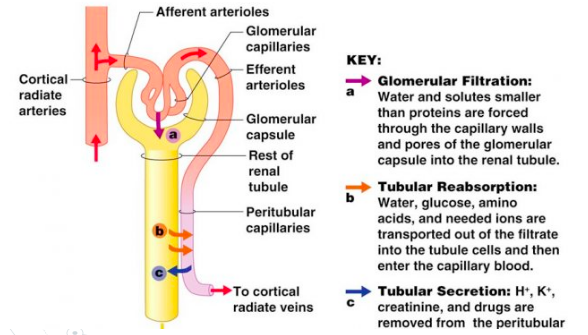
Urinary System Part 2: Urine Formation – The Biology Classroom 11.1 Describe the roles of agonists, antagonists and synergists. 11.2 Explain the organization of muscle fascicles and their role in generating force. … resulting in the formation of urine. Many substances that need to be removed from the body still remain in the blood. The tubule cells remove them from the blood and secrete them into the
Source Image: blogs.ubc.ca
Download Image
EasyElimu on X: “Describe the process of urine formation in the mammalian kidneys – KCSE Biology Essays https://t.co/k4Klvqg8GS #HeavenlyFocusedChristian https://t.co/Xn8D6RzyTX” / X The formation process occurs in 3 steps or phases: Glomerular Filtration Tubular Reabsorption Tubular Secretion Anatomy of the Nephron (Source: sites.google.com) The anatomy of the nephron is important to understand the urine formation process. Each nephron is made up of two parts: Renal Corpuscle Renal Tubule

Source Image: twitter.com
Download Image
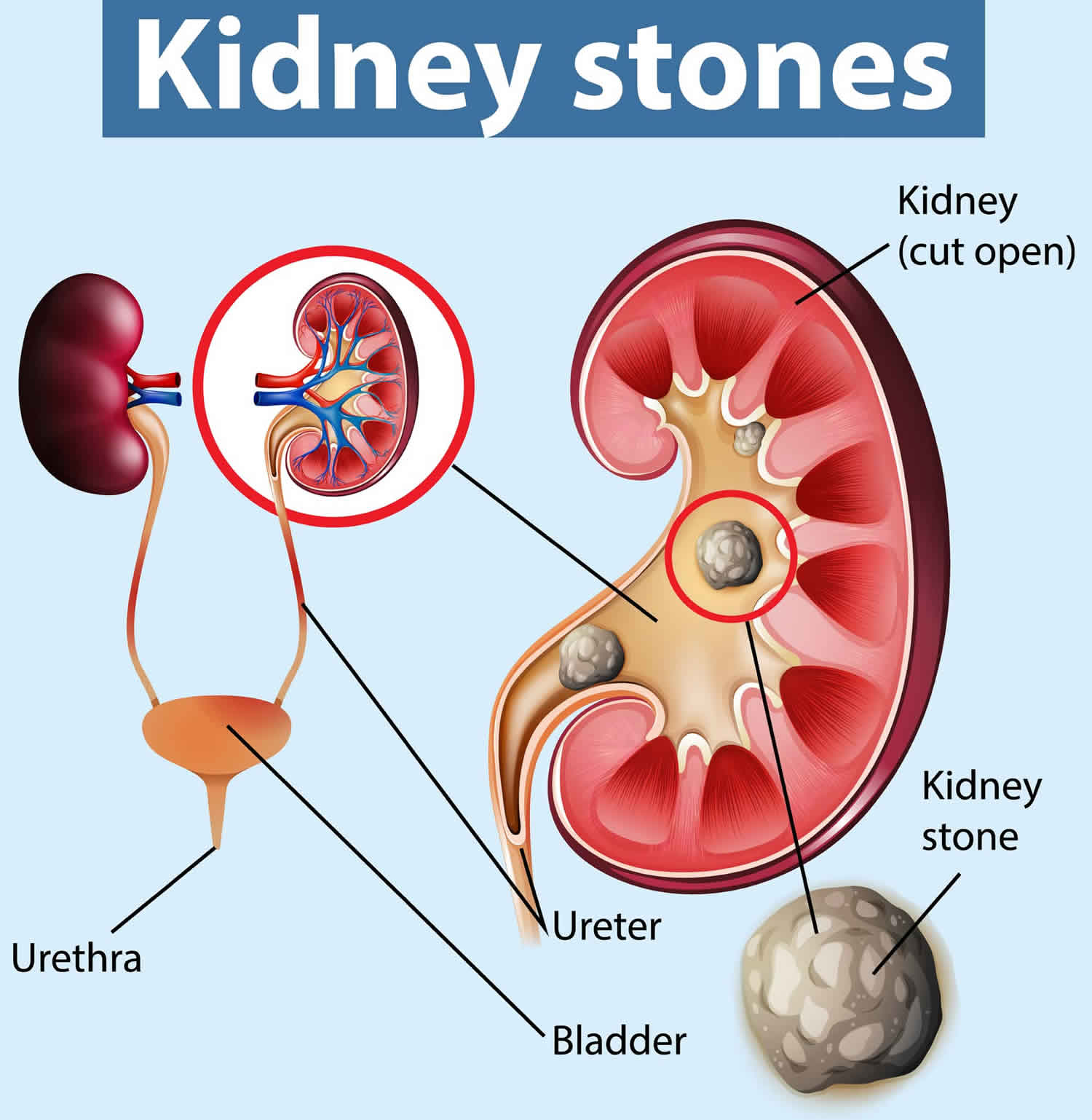
Kidney stones, causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment & prognosis Nephrons: The Functional Unit. Nephrons take a simple filtrate of the blood and modify it into urine. Many changes take place in the different parts of the nephron before urine is created for disposal. The term forming urine will be used hereafter to describe the filtrate as it is modified into true urine.
Source Image: healthjade.net
Download Image
Formation of Urine – Nephron Function, Animation. – YouTube
Kidney stones, causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment & prognosis Physiology of Urine formation. There are three stages involved in the process of urine formation. They are-. 1. Glomerular filtration or ultra-filtration. 2. Selective reabsorption. 3. Tubular secretion.
Understanding Urine Formation: A Comprehensive Flow Chart EasyElimu on X: “Describe the process of urine formation in the mammalian kidneys – KCSE Biology Essays https://t.co/k4Klvqg8GS #HeavenlyFocusedChristian https://t.co/Xn8D6RzyTX” / X 11.1 Describe the roles of agonists, antagonists and synergists. 11.2 Explain the organization of muscle fascicles and their role in generating force. … resulting in the formation of urine. Many substances that need to be removed from the body still remain in the blood. The tubule cells remove them from the blood and secrete them into the