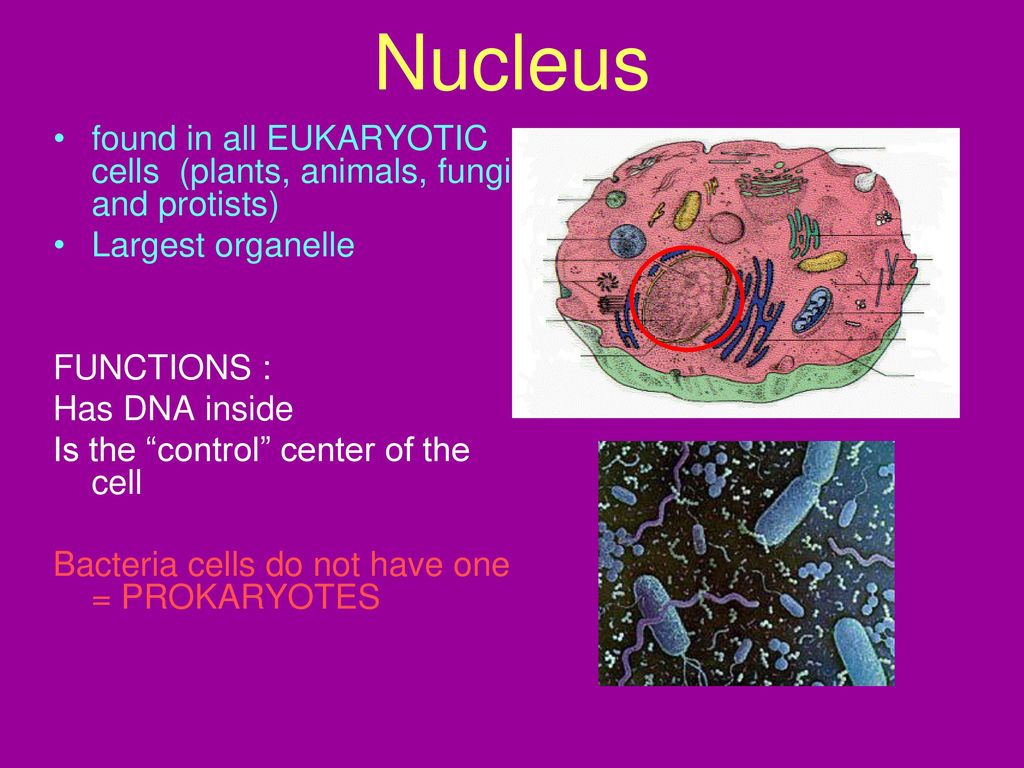
The nucleus of a cell, an organelle found in almost all eukaryotic organisms, is the command and control center of the cell. The nucleus stores the organism’s genetic material and communicates commands concerning general cell behavior to the rest of the cell using molecular messengers.
What is a nucleus? What are some examples? – Quora
Oct 31, 2023The cell nucleus is a membrane-bound structure that contains the cell’s hereditary information and controls the cell’s growth and reproduction. It is the command center of a eukaryotic cell and is commonly the most prominent organelle in a cell accounting for about 10 percent of the cell’s volume. In general, a eukaryotic cell has only
Source Image: slideplayer.com
Download Image
The cell nucleus (from Latin nucleus or nuculeus ‘kernel, seed’; pl.: nuclei) is a membrane-bound organelle found in eukaryotic cells. Eukaryotic cells usually have a single nucleus, but a few cell types, such as mammalian red blood cells, have no nuclei, and a few others including osteoclasts have many.
Source Image: visualcapitalist.com
Download Image
Schwann Cell | Definition, Function, & Location May 15, 2022Chromatin. The nucleus contains the chromosomes of the cell. Each chromosome consists of a single molecule of DNA complexed with an equal mass of proteins. Collectively, the DNA of the nucleus with its associated proteins is called chromatin. Most of the protein consists of multiple copies of 5 kinds of histones.
Source Image: vedantu.com
Download Image
What Is Not Found In The Nucleus
May 15, 2022Chromatin. The nucleus contains the chromosomes of the cell. Each chromosome consists of a single molecule of DNA complexed with an equal mass of proteins. Collectively, the DNA of the nucleus with its associated proteins is called chromatin. Most of the protein consists of multiple copies of 5 kinds of histones. Key points: All cells have a cell membrane that separates the inside and the outside of the cell, and controls what goes in and comes out. The cell membrane surrounds a cell’s cytoplasm, which is a jelly-like substance containing the cell’s parts. Cells contain parts called organelles. Each organelle carries out a specific function in the cell.
True nucleus is absent in A. Green algaeB. FungiC. LichensD. Bacteria
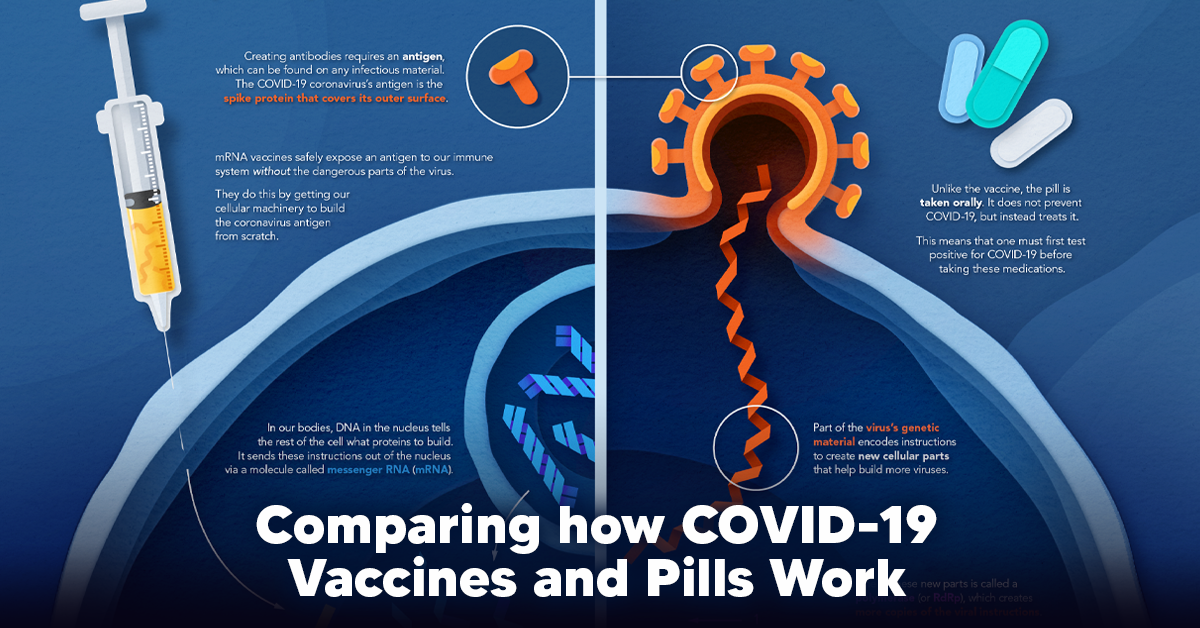
The nucleus. The nucleus (plural, nuclei) houses the cell’s genetic material, or DNA, and is also the site of synthesis for ribosomes, the cellular machines that assemble proteins. Inside the nucleus, chromatin (DNA wrapped around proteins, described further below) is stored in a gel-like substance called nucleoplasm. Carbon Unveiled: Advanced Simulations Reveal Nuclear Secrets
Source Image: scitechdaily.com
Download Image
Premium Vector | Neuron nucleus cell body parts anatomy The nucleus. The nucleus (plural, nuclei) houses the cell’s genetic material, or DNA, and is also the site of synthesis for ribosomes, the cellular machines that assemble proteins. Inside the nucleus, chromatin (DNA wrapped around proteins, described further below) is stored in a gel-like substance called nucleoplasm.

Source Image: freepik.com
Download Image
What is a nucleus? What are some examples? – Quora The nucleus of a cell, an organelle found in almost all eukaryotic organisms, is the command and control center of the cell. The nucleus stores the organism’s genetic material and communicates commands concerning general cell behavior to the rest of the cell using molecular messengers.
Source Image: quora.com
Download Image
Schwann Cell | Definition, Function, & Location The cell nucleus (from Latin nucleus or nuculeus ‘kernel, seed’; pl.: nuclei) is a membrane-bound organelle found in eukaryotic cells. Eukaryotic cells usually have a single nucleus, but a few cell types, such as mammalian red blood cells, have no nuclei, and a few others including osteoclasts have many.

Source Image: simplypsychology.org
Download Image
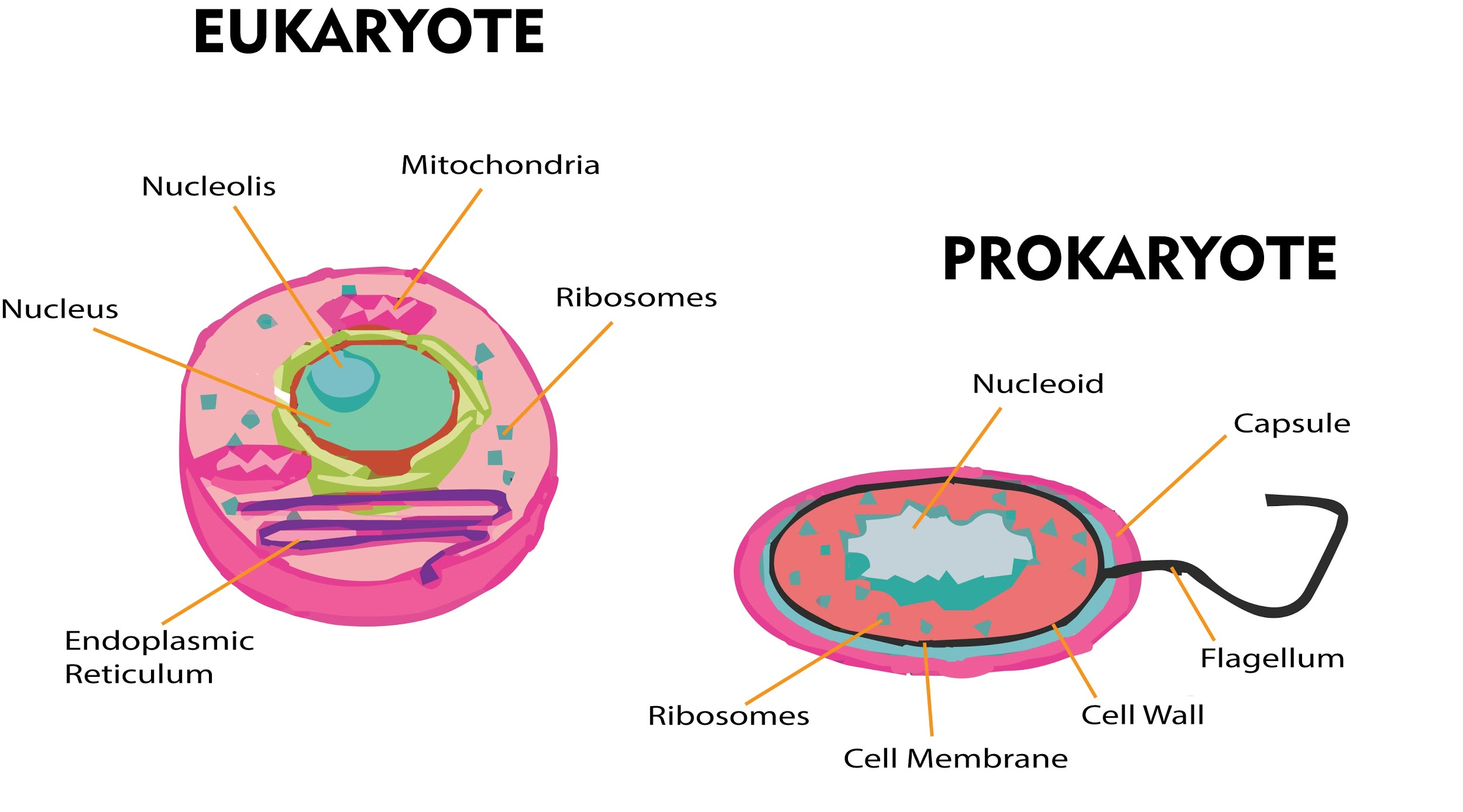
Cells cram DNA into the nucleus in two distinct ways Updated March 13, 2018 By Bailey Rodriguez In 1665, Robert Hooke, a British scientist, discovered cells, the tiny compartments of DNA and proteins. Looking at a piece of cork under a microscope, Hooke coined the term “cells” for the different chambers that make up the piece of cork. The two types of cells are eukaryotes and prokaryotics.

Source Image: sciencenews.org
Download Image
What is the difference between the hypothalamus and the medulla oblongata? – Quora May 15, 2022Chromatin. The nucleus contains the chromosomes of the cell. Each chromosome consists of a single molecule of DNA complexed with an equal mass of proteins. Collectively, the DNA of the nucleus with its associated proteins is called chromatin. Most of the protein consists of multiple copies of 5 kinds of histones.
Source Image: quora.com
Download Image
Hypothalamic nuclei, illustration – Stock Image – F040/4136 – Science Photo Library Key points: All cells have a cell membrane that separates the inside and the outside of the cell, and controls what goes in and comes out. The cell membrane surrounds a cell’s cytoplasm, which is a jelly-like substance containing the cell’s parts. Cells contain parts called organelles. Each organelle carries out a specific function in the cell.

Source Image: sciencephoto.com
Download Image
Premium Vector | Neuron nucleus cell body parts anatomy
Hypothalamic nuclei, illustration – Stock Image – F040/4136 – Science Photo Library Oct 31, 2023The cell nucleus is a membrane-bound structure that contains the cell’s hereditary information and controls the cell’s growth and reproduction. It is the command center of a eukaryotic cell and is commonly the most prominent organelle in a cell accounting for about 10 percent of the cell’s volume. In general, a eukaryotic cell has only
Schwann Cell | Definition, Function, & Location What is the difference between the hypothalamus and the medulla oblongata? – Quora Updated March 13, 2018 By Bailey Rodriguez In 1665, Robert Hooke, a British scientist, discovered cells, the tiny compartments of DNA and proteins. Looking at a piece of cork under a microscope, Hooke coined the term “cells” for the different chambers that make up the piece of cork. The two types of cells are eukaryotes and prokaryotics.